Configuration de SAMBA, je n'y arrive plus [Réglé]
Adrien.D Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Adrien.D
- Inscrit le : 30/05/2011
- Site internet
- Groupes :
je vous interpelle à propos de samba, je n'arrive plus à la configurer.
Voici ce qu'il me dit:
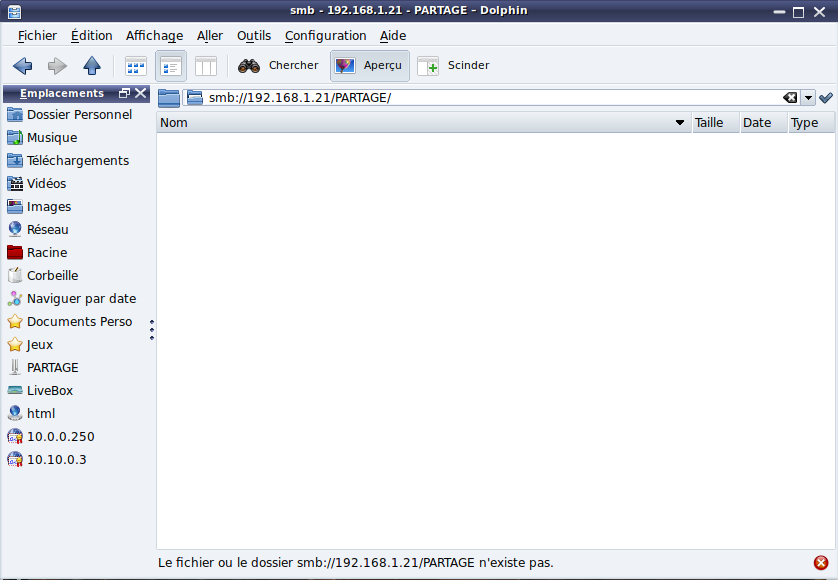
Pourtant le partage est bien créé, voici des infos concernant la partie du partage du smb.conf
Caché :
[PARTAGE]
path = /home/adrien/PARTAGE
comment = "PartageWindows"
browseable = yes
hide dot files = yes
read only = no
public = yes
writable = yes
path = /home/adrien/PARTAGE
comment = "PartageWindows"
browseable = yes
hide dot files = yes
read only = no
public = yes
writable = yes
Et voici les permissions:
Caché :
4 [21:20:02] root@mageia: /home/adrien # ll . | grep PARTAGE
drwxrwxrwx 4 adrien adrien 4096 déc. 7 15:39 PARTAGE/
drwxrwxrwx 4 adrien adrien 4096 déc. 7 15:39 PARTAGE/
Ca fait une semaine que je me prends le choux avec cela !
Une idée ?
Config : PC Fixe : X470 GAMING PRO- AMD Ryzen 5 2600X - 16Go RAM - Radeon RX 560 (Pilote libre) - Gentoo Linux - GNOME Desktop - Kernel 5.10 LTS
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !

OPS56 Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre OPS56
- Inscrit le : 18/11/2008
- Groupes :

As tu essayé en désactivant le parefeu pour voir ?
Sinon, essaye de redémarrer ta box. Ma livebox me fait ça de temps en temps ! Tout marche bien sauf les partages entre PC. Je la reboot et c'est Ok

@+

Dell G3-15 Intel Corei7 - 16Go Ram - Nvidia GTX1660 Ti (Tri boot Mageia 9- 64 bits / Linux Mint 20 Cinamon/ Windows 10)
Core i5 760 - 8Go Ram - Nvidia Gforce 450 - (Triple boot Mageia 9-64 bits - Plasma 5 / Mint 20 Cinamon / Open Suse Tumbleweed - Plasma 5)
Yopman Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Yopman
- Inscrit le : 24/12/2008
- Site internet
- Groupes :
-
Administrateur

Bon en premier lieu, j'ai déplacé le sujet dans la section réseau (cela me semblait plus approprié)
Ensuite, il est vrai, mais tu as du le faire, qu'il faut régler ton pare feu personnel sur le "serveur samba"
Pour info de la configuration, ta structure est un PC Linux Samba serveur qui partage des fichiers avec d'autres PC Linux et Windows ?
Eventuellement, peux tu nous mettre ton smb.conf en totalité
Merci,
@+

Adrien.D Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Adrien.D
- Inscrit le : 30/05/2011
- Site internet
- Groupes :
smb.conf:
Caché :
2 [15:03:03] root@mageia: ~ # cat /etc/samba/smb.conf
# This is the main Samba configuration file. You should read the
# smb.conf(5) manual page in order to understand the options listed
# here. Samba has a huge number of configurable options (perhaps too
# many!) most of which are not shown in this example
#
# Any line which starts with a ; (semi-colon) or a # (hash)
# is a comment and is ignored. In this example we will use a #
# for commentry and a ; for parts of the config file that you
# may wish to enable
#
# NOTE: Whenever you modify this file you should run the command "testparm"
# to check that you have not made any basic syntactic errors.
#
#======================= Global Settings =====================================
[global]
# 1. Server Naming Options:
# workgroup = NT-Domain-Name or Workgroup-Name
workgroup = WORKGROUP
# netbios name is the name you will see in "Network Neighbourhood",
# but defaults to your hostname
# netbios name = <name_of_this_server>
# server string is the equivalent of the NT Description field
server string = %h
# Message command is run by samba when a "popup" message is sent to it.
# The example below is for use with LinPopUp:
; message command = /usr/bin/linpopup "%f" "%m" %s; rm %s
# 2. Printing Options:
# Required to load all CUPS printers
printcap name = cups
load printers = yes
# printcap cache time, so samba will automatically load new cups printers
printcap cache time = 60
# It should not be necessary to spell out the print system type unless
# yours is non-standard. Currently supported print systems include:
# bsd, sysv, plp, lprng, aix, hpux, qnx, cups
printing = cups
# Samba 2.2 supports the Windows NT-style point-and-print feature. To
# use this, you need to be able to upload print drivers to the samba
# server. The printer admins (or root) may install drivers onto samba.
# Note that this feature uses the print$ share, so you will need to
# enable it below.
# Printer admins are now defined by granting the SePrintOperatorPrivilege, ie:
# run: net rpc rights grant 'DOMAINPrinter Operators' SePrintOperatorPrivilege
# 3. Logging Options:
# this tells Samba to use a separate log file for each machine
# that connects
log file = /var/log/samba/%m.log
# Put a capping on the size of the log files (in Kb).
max log size = 50
# Uncomment this if you want a guest account, you must add this to /etc/passwd
# otherwise the user "nobody" is used
# guest account = pcguest
# Allow users to map to guest:
map to guest = bad user
# Security mode. Most people will want user level security. See
# security_level.txt for details.
security = user
# Use password server option only with security = server or security = domain
# When using security = domain, you should use password server = *
# password server = <NT-Server-Name>
# password server = *
# Password Level allows matching of _n_ characters of the password for
# all combinations of upper and lower case.
# password level = 8
# username level = 8
# You may wish to use password encryption. Please read
# ENCRYPTION.txt, Win95.txt and WinNT.txt in the Samba documentation.
# Do not enable this option unless you have read those documents
# Encrypted passwords are required for any use of samba in a Windows NT domain
# The smbpasswd file is only required by a server doing authentication, thus
# members of a domain do not need one.
encrypt passwords = yes
smb passwd file = /etc/samba/smbpasswd
# The following are needed to allow password changing from Windows to
# also update the Linux system password.
# NOTE: Use these with 'encrypt passwords' and 'smb passwd file' above.
# NOTE2: You do NOT need these to allow workstations to change only
# the encrypted SMB passwords. They allow the Unix password
# to be kept in sync with the SMB password.
; unix password sync = Yes
# You either need to setup a passwd program and passwd chat, or
# enable pam password change
; pam password change = yes
# passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd '%u'
; passwd chat = *New*UNIX*password* %nn *Re*ype*new*UNIX*password* %nn
;*passwd:*all*authentication*tokens*updated*successfully*
# Unix users can map to different SMB User names
; username map = /etc/samba/smbusers
# Using the following line enables you to customise your configuration
# on a per machine basis. The %m gets replaced with the netbios name
# of the machine that is connecting
# include = /etc/samba/smb.conf.%m
# Options for using winbind. Winbind allows you to do all account and
# authentication from a Windows or samba domain controller, creating
# accounts on the fly, and maintaining a mapping of Windows RIDs to unix uid's
# and gid's. winbind uid and winbind gid are the only required parameters.
#
# winbind uid is the range of uid's winbind can use when mapping RIDs to uid's
# idmap uid = 10000-20000
#
# winbind gid is the range of uid's winbind can use when mapping RIDs to gid's
# idmap gid = 10000-20000
#
# winbind separator is the character a user must use between their domain
# name and username, defaults to ""
# winbind separator = +
#
# winbind use default domain allows you to have winbind return usernames
# in the form user instead of DOMAIN+user for the domain listed in the
# workgroup parameter.
# winbind use default domain = yes
#
# template homedir determines the home directory for winbind users, with
# %D expanding to their domain name and %U expanding to their username:
# template homedir = /home/%D/%U
# When using winbind, you may want to have samba create home directories
# on the fly for authenticated users. Ensure that /etc/pam.d/samba is
# using 'service=system-auth-winbind' in pam_stack modules, and then
# enable obedience of pam restrictions below:
# obey pam restrictions = yes
#
# template shell determines the shell users authenticated by winbind get
# template shell = /bin/bash
# 5. Browser Control and Networking Options:
# Configure Samba to use multiple interfaces
# If you have multiple network interfaces then you must list them
# here. See the man page for details.
# interfaces = 192.168.12.2/24 192.168.13.2/24
# Configure remote browse list synchronisation here
# request announcement to, or browse list sync from:
# a specific host or from / to a whole subnet (see below)
# remote browse sync = 192.168.3.25 192.168.5.255
# Cause this host to announce itself to local subnets here
# remote announce = 192.168.1.255 192.168.2.44
# set local master to no if you don't want Samba to become a master
# browser on your network. Otherwise the normal election rules apply
# local master = no
# OS Level determines the precedence of this server in master browser
# elections. The default value should be reasonable
# os level = 33
# Domain Master specifies Samba to be the Domain Master Browser. This
# allows Samba to collate browse lists between subnets. Don't use this
# if you already have a Windows NT domain controller doing this job
# domain master = yes
# Preferred Master causes Samba to force a local browser election on startup
# and gives it a slightly higher chance of winning the election
# preferred master = yes
# 6. Domain Control Options:
# Enable this if you want Samba to be a domain logon server for
# Windows95 workstations or Primary Domain Controller for WinNT and Win2k
# domain logons = yes
# if you enable domain logons then you may want a per-machine or
# per user logon script
# run a specific logon batch file per workstation (machine)
# logon script = %m.bat
# run a specific logon batch file per username
# logon script = %u.bat
# Where to store roaming profiles for WinNT and Win2k
# %L substitutes for this servers netbios name, %u is username
# You must uncomment the [Profiles] share below
# logon path = \%LProfiles%u
# Where to store roaming profiles for Win9x. Be careful with this as it also
# impacts where Win2k finds it's /HOME share
# logon home = \%L%u.profile
# The add user script is used by a domain member to add local user accounts
# that have been authenticated by the domain controller, or when adding
# users via the Windows NT Tools (ie User Manager for Domains).
# Scripts for file (passwd, smbpasswd) backend:
# add user script = /usr/sbin/useradd -s /bin/false '%u'
# delete user script = /usr/sbin/userdel '%s'
# add user to group script = /usr/bin/gpasswd -a '%u' '%g'
# delete user from group script = /usr/bin/gpasswd -d '%u' '%g'
# set primary group script = /usr/sbin/usermod -g '%g' '%u'
# add group script = /usr/sbin/groupadd %g && getent group '%g'|awk -F: '{print $3}'
# delete group script = /usr/sbin/groupdel '%g'
# Scripts for LDAP backend (assumes nss_ldap is in use on the domain controller,
# and needs configuration in smbldap_conf.pm
# add user script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-useradd -m '%u'
# delete user script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-userdel '%u'
# add user to group script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-groupmod -m '%u' '%g'
# delete user from group script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-groupmod -x '%u' '%g'
# set primary group script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-usermod -g '%g' '%u'
# add group script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-groupadd '%g' && /usr/sbin/smbldap-groupshow %g|awk '/^gidNumber:/ {print $2}'
# delete group script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-groupdel '%g'
# The add machine script is use by a samba server configured as a domain
# controller to add local machine accounts when adding machines to the domain.
# The script must work from the command line when replacing the macros,
# or the operation will fail. Check that groups exist if forcing a group.
# Script for domain controller for adding machines:
# add machine script = /usr/sbin/useradd -d /dev/null -g machines -c 'Machine Account' -s /bin/false -M '%u'
# Script for domain controller with LDAP backend for adding machines (please
# configure in /etc/samba/smbldap_conf.pm first):
# add machine script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-useradd -w -d /dev/null -c 'Machine Account' -s /bin/false '%u'
# Domain groups:
# Domain groups are now configured by using the 'net groupmap' tool
# Enable priveleges, ie allowing members of Domain Admins to join machines
# to the domain
# enable privileges = yes
# Samba Password Database configuration:
# Samba now has runtime-configurable password database backends. Multiple
# passdb backends may be used, but users will only be added to the first one
# Default:
# passdb backend = tdbsam
# TDB backen with fallback to smbpasswd and guest
# passdb backend = tdbsam smbpasswd guest
# LDAP with fallback to smbpasswd guest
# Enable SSL by using an ldaps url, or enable tls with 'ldap ssl' below.
# passdb backend = ldapsam:ldaps://ldap.mydomain.com smbpasswd guest
# Use the samba2 LDAP schema:
# passdb backend = ldapsam_compat:ldaps://ldap.mydomain.com smbpasswd guest
# Idmap settings (set idmap uid and idmap gid above):
# Idmap backend to use:
# idmap backend = ldap:ldap://ldap.mydomain.com
# LDAP configuration for Domain Controlling:
# The account (dn) that samba uses to access the LDAP server
# This account needs to have write access to the LDAP tree
# You will need to give samba the password for this dn, by
# running 'smbpasswd -w mypassword'
# ldap admin dn = cn=root,dc=mydomain,dc=com
# ldap ssl = start_tls
# start_tls should run on 389, but samba defaults incorrectly to 636
# ldap port = 389
# ldap suffix = dc=mydomain,dc=com
# Seperate suffixes are available for machines, users, groups, and idmap, if
# ldap suffix appears first, it is appended to the specific suffix.
# Example for a unix-ish directory layout:
# ldap machine suffix = ou=Hosts
# ldap user suffix = ou=People
# ldap group suffix = ou=Group
# ldap idmap suffix = ou=Idmap
# Example for AD-ish layout:
# ldap machine suffix = cn=Computers
# ldap user suffix = cn=Users
# ldap group suffix = cn=Groups
# ldap idmap suffix = cn=Idmap
# 7. Name Resolution Options:
# All NetBIOS names must be resolved to IP Addresses
# 'Name Resolve Order' allows the named resolution mechanism to be specified
# the default order is "host lmhosts wins bcast". "host" means use the unix
# system gethostbyname() function call that will use either /etc/hosts OR
# DNS or NIS depending on the settings of /etc/host.config, /etc/nsswitch.conf
# and the /etc/resolv.conf file. "host" therefore is system configuration
# dependant. This parameter is most often of use to prevent DNS lookups
# in order to resolve NetBIOS names to IP Addresses. Use with care!
# The example below excludes use of name resolution for machines that are NOT
# on the local network segment
# - OR - are not deliberately to be known via lmhosts or via WINS.
# name resolve order = wins lmhosts bcast
# Windows Internet Name Serving Support Section:
# WINS Support - Tells the NMBD component of Samba to enable it's WINS Server
# wins support = yes
# WINS Server - Tells the NMBD components of Samba to be a WINS Client
# Note: Samba can be either a WINS Server, or a WINS Client, but NOT both
# wins server = w.x.y.z
# WINS Proxy - Tells Samba to answer name resolution queries on
# behalf of a non WINS capable client, for this to work there must be
# at least one WINS Server on the network. The default is NO.
# wins proxy = yes
# DNS Proxy - tells Samba whether or not to try to resolve NetBIOS names
# via DNS nslookups. The built-in default for versions 1.9.17 is yes,
# this has been changed in version 1.9.18 to no.
dns proxy = no
netbios name = MAGEIA
# 8. File Naming Options:
# Case Preservation can be handy - system default is _no_
# NOTE: These can be set on a per share basis
# preserve case = no
# short preserve case = no
# Default case is normally upper case for all DOS files
# default case = lower
# Be very careful with case sensitivity - it can break things!
# case sensitive = no
# Enabling internationalization:
# you can match a Windows code page with a UNIX character set.
# Windows: 437 (US), 737 (GREEK), 850 (Latin1 - Western European),
# 852 (Eastern Eu.), 861 (Icelandic), 932 (Cyrillic - Russian),
# 936 (Japanese - Shift-JIS), 936 (Simpl. Chinese), 949 (Korean Hangul),
# 950 (Trad. Chin.).
# UNIX: ISO8859-1 (Western European), ISO8859-2 (Eastern Eu.),
# ISO8859-5 (Russian Cyrillic), KOI8-R (Alt-Russ. Cyril.)
# This is an example for french users:
# dos charset = 850
# unix charset = ISO8859-1
#============================ Share Definitions ==============================
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
browseable = no
writable = yes
# You can enable VFS recycle bin and on-access virus-scanning on a per
# share basis:
# Uncomment the next 2 lines (make sure you create a .recycle folder in
# the base of the share and ensure all users will have write access to it.
# For virus scanning, install samba-vscan-clamav and ensure the clamd service
# is running
# vfs objects = vscan-clamav recycle
# vscan-clamav: config-file = /etc/samba/vscan-clamav.conf
# Un-comment the following and create the netlogon directory for Domain Logons
# [netlogon]
# comment = Network Logon Service
# path = /var/lib/samba/netlogon
# guest ok = yes
# writable = no
#Uncomment the following 2 lines if you would like your login scripts to
#be created dynamically by ntlogon (check that you have it in the correct
#location (the default of the ntlogon rpm available in contribs)
#root preexec = /usr/bin/ntlogon -u '%u' -g '%g' -o %a -d /var/lib/samba/netlogon/
#root postexec = rm -f '/var/lib/samba/netlogon/%u.bat'
# Un-comment the following to provide a specific roving profile share
# the default is to use the user's home directory
#[Profiles]
# path = /var/lib/samba/profiles
# browseable = no
# guest ok = yes
# writable = yes
# This script can be enabled to create profile directories on the fly
# You may want to turn off guest acces if you enable this, as it
# hasn't been thoroughly tested.
#root preexec = PROFILE='/var/lib/samba/profiles/%u'; if [ ! -e $PROFILE ];
# then mkdir -pm700 $PROFILE; chown '%u':'%g' $PROFILE;fi
# If you want read-only profiles, fake permissions so windows clients think
# they have written to the files
# vfs objects = fake_perms
# NOTE: If you have a CUPS print system there is no need to
# specifically define each individual printer.
# You must configure the samba printers with the appropriate Windows
# drivers on your Windows clients or upload the printer driver to the
# server from Windows (NT/2000/XP). On the Samba server no filtering is
# done. If you wish that the server provides the driver and the clients
# send PostScript ("Generic PostScript Printer" under Windows), you have
# to use 'printcap name = cups' or swap the 'print command' line below
# with the commented one. Note that print commands only work if not using
# 'printing=cups'
[printers]
comment = All Printers
path = /var/spool/samba
browseable = no
# to allow user 'guest account' to print.
guest ok = yes
writable = no
printable = yes
create mode = 0700
# =====================================
# print command: see above for details.
# =====================================
print command = lpr-cups -P %p -o raw %s -r # using client side printer drivers.
# print command = lpr-cups -P %p %s # using cups own drivers (use generic PostScript on clients).
# If you install drivers on the server, you will want to uncomment this so
# clients request the driver
use client driver = yes
# This share is used for Windows NT-style point-and-print support.
# To be able to install drivers, you need to be either root, or listed
# in the printer admin parameter above. Note that you also need write access
# to the directory and share definition to be able to upload the drivers.
# For more information on this, please see the Printing Support Section of
# /usr/share/doc/samba-<version>/docs/Samba-HOWTO-Collection.pdf
#
# A special case is using the CUPS Windows Postscript driver, which allows
# all features available via CUPS on the client, by publishing the ppd file
# and the cups driver by using the 'cupsaddsmb' tool. This requires the
# installation of the CUPS driver (http://www.cups.org/windows.php)
# on the server, but doesn't require you to use Windows at all :-).
[print$]
path = /var/lib/samba/printers
browseable = yes
write list = @adm root
guest ok = yes
inherit permissions = yes
# Settings suitable for Winbind:
# write list = @"Domain Admins" root
# force group = +@"Domain Admins"
# A useful application of samba is to make a PDF-generation service
# To streamline this, install windows postscript drivers (preferably colour)
# on the samba server, so that clients can automatically install them.
# Note that this only works if 'printing' is *not* set to 'cups'
[pdf-gen]
path = /var/tmp
guest ok = No
printable = Yes
comment = PDF Generator (only valid users)
printing = bsd
#print command = /usr/share/samba/scripts/print-pdf file path win_path recipient IP &
print command = /usr/share/samba/scripts/print-pdf "%s" "%H" "//%L/%u" "%m" "%I" "%J" &
lpq command = /bin/true
[PARTAGE]
path = /home/adrien/PARTAGE
comment = "PartageWindows"
browseable = yes
hide dot files = yes
read only = no
public = yes
writable = yes
# This is the main Samba configuration file. You should read the
# smb.conf(5) manual page in order to understand the options listed
# here. Samba has a huge number of configurable options (perhaps too
# many!) most of which are not shown in this example
#
# Any line which starts with a ; (semi-colon) or a # (hash)
# is a comment and is ignored. In this example we will use a #
# for commentry and a ; for parts of the config file that you
# may wish to enable
#
# NOTE: Whenever you modify this file you should run the command "testparm"
# to check that you have not made any basic syntactic errors.
#
#======================= Global Settings =====================================
[global]
# 1. Server Naming Options:
# workgroup = NT-Domain-Name or Workgroup-Name
workgroup = WORKGROUP
# netbios name is the name you will see in "Network Neighbourhood",
# but defaults to your hostname
# netbios name = <name_of_this_server>
# server string is the equivalent of the NT Description field
server string = %h
# Message command is run by samba when a "popup" message is sent to it.
# The example below is for use with LinPopUp:
; message command = /usr/bin/linpopup "%f" "%m" %s; rm %s
# 2. Printing Options:
# Required to load all CUPS printers
printcap name = cups
load printers = yes
# printcap cache time, so samba will automatically load new cups printers
printcap cache time = 60
# It should not be necessary to spell out the print system type unless
# yours is non-standard. Currently supported print systems include:
# bsd, sysv, plp, lprng, aix, hpux, qnx, cups
printing = cups
# Samba 2.2 supports the Windows NT-style point-and-print feature. To
# use this, you need to be able to upload print drivers to the samba
# server. The printer admins (or root) may install drivers onto samba.
# Note that this feature uses the print$ share, so you will need to
# enable it below.
# Printer admins are now defined by granting the SePrintOperatorPrivilege, ie:
# run: net rpc rights grant 'DOMAINPrinter Operators' SePrintOperatorPrivilege
# 3. Logging Options:
# this tells Samba to use a separate log file for each machine
# that connects
log file = /var/log/samba/%m.log
# Put a capping on the size of the log files (in Kb).
max log size = 50
# Uncomment this if you want a guest account, you must add this to /etc/passwd
# otherwise the user "nobody" is used
# guest account = pcguest
# Allow users to map to guest:
map to guest = bad user
# Security mode. Most people will want user level security. See
# security_level.txt for details.
security = user
# Use password server option only with security = server or security = domain
# When using security = domain, you should use password server = *
# password server = <NT-Server-Name>
# password server = *
# Password Level allows matching of _n_ characters of the password for
# all combinations of upper and lower case.
# password level = 8
# username level = 8
# You may wish to use password encryption. Please read
# ENCRYPTION.txt, Win95.txt and WinNT.txt in the Samba documentation.
# Do not enable this option unless you have read those documents
# Encrypted passwords are required for any use of samba in a Windows NT domain
# The smbpasswd file is only required by a server doing authentication, thus
# members of a domain do not need one.
encrypt passwords = yes
smb passwd file = /etc/samba/smbpasswd
# The following are needed to allow password changing from Windows to
# also update the Linux system password.
# NOTE: Use these with 'encrypt passwords' and 'smb passwd file' above.
# NOTE2: You do NOT need these to allow workstations to change only
# the encrypted SMB passwords. They allow the Unix password
# to be kept in sync with the SMB password.
; unix password sync = Yes
# You either need to setup a passwd program and passwd chat, or
# enable pam password change
; pam password change = yes
# passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd '%u'
; passwd chat = *New*UNIX*password* %nn *Re*ype*new*UNIX*password* %nn
;*passwd:*all*authentication*tokens*updated*successfully*
# Unix users can map to different SMB User names
; username map = /etc/samba/smbusers
# Using the following line enables you to customise your configuration
# on a per machine basis. The %m gets replaced with the netbios name
# of the machine that is connecting
# include = /etc/samba/smb.conf.%m
# Options for using winbind. Winbind allows you to do all account and
# authentication from a Windows or samba domain controller, creating
# accounts on the fly, and maintaining a mapping of Windows RIDs to unix uid's
# and gid's. winbind uid and winbind gid are the only required parameters.
#
# winbind uid is the range of uid's winbind can use when mapping RIDs to uid's
# idmap uid = 10000-20000
#
# winbind gid is the range of uid's winbind can use when mapping RIDs to gid's
# idmap gid = 10000-20000
#
# winbind separator is the character a user must use between their domain
# name and username, defaults to ""
# winbind separator = +
#
# winbind use default domain allows you to have winbind return usernames
# in the form user instead of DOMAIN+user for the domain listed in the
# workgroup parameter.
# winbind use default domain = yes
#
# template homedir determines the home directory for winbind users, with
# %D expanding to their domain name and %U expanding to their username:
# template homedir = /home/%D/%U
# When using winbind, you may want to have samba create home directories
# on the fly for authenticated users. Ensure that /etc/pam.d/samba is
# using 'service=system-auth-winbind' in pam_stack modules, and then
# enable obedience of pam restrictions below:
# obey pam restrictions = yes
#
# template shell determines the shell users authenticated by winbind get
# template shell = /bin/bash
# 5. Browser Control and Networking Options:
# Configure Samba to use multiple interfaces
# If you have multiple network interfaces then you must list them
# here. See the man page for details.
# interfaces = 192.168.12.2/24 192.168.13.2/24
# Configure remote browse list synchronisation here
# request announcement to, or browse list sync from:
# a specific host or from / to a whole subnet (see below)
# remote browse sync = 192.168.3.25 192.168.5.255
# Cause this host to announce itself to local subnets here
# remote announce = 192.168.1.255 192.168.2.44
# set local master to no if you don't want Samba to become a master
# browser on your network. Otherwise the normal election rules apply
# local master = no
# OS Level determines the precedence of this server in master browser
# elections. The default value should be reasonable
# os level = 33
# Domain Master specifies Samba to be the Domain Master Browser. This
# allows Samba to collate browse lists between subnets. Don't use this
# if you already have a Windows NT domain controller doing this job
# domain master = yes
# Preferred Master causes Samba to force a local browser election on startup
# and gives it a slightly higher chance of winning the election
# preferred master = yes
# 6. Domain Control Options:
# Enable this if you want Samba to be a domain logon server for
# Windows95 workstations or Primary Domain Controller for WinNT and Win2k
# domain logons = yes
# if you enable domain logons then you may want a per-machine or
# per user logon script
# run a specific logon batch file per workstation (machine)
# logon script = %m.bat
# run a specific logon batch file per username
# logon script = %u.bat
# Where to store roaming profiles for WinNT and Win2k
# %L substitutes for this servers netbios name, %u is username
# You must uncomment the [Profiles] share below
# logon path = \%LProfiles%u
# Where to store roaming profiles for Win9x. Be careful with this as it also
# impacts where Win2k finds it's /HOME share
# logon home = \%L%u.profile
# The add user script is used by a domain member to add local user accounts
# that have been authenticated by the domain controller, or when adding
# users via the Windows NT Tools (ie User Manager for Domains).
# Scripts for file (passwd, smbpasswd) backend:
# add user script = /usr/sbin/useradd -s /bin/false '%u'
# delete user script = /usr/sbin/userdel '%s'
# add user to group script = /usr/bin/gpasswd -a '%u' '%g'
# delete user from group script = /usr/bin/gpasswd -d '%u' '%g'
# set primary group script = /usr/sbin/usermod -g '%g' '%u'
# add group script = /usr/sbin/groupadd %g && getent group '%g'|awk -F: '{print $3}'
# delete group script = /usr/sbin/groupdel '%g'
# Scripts for LDAP backend (assumes nss_ldap is in use on the domain controller,
# and needs configuration in smbldap_conf.pm
# add user script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-useradd -m '%u'
# delete user script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-userdel '%u'
# add user to group script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-groupmod -m '%u' '%g'
# delete user from group script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-groupmod -x '%u' '%g'
# set primary group script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-usermod -g '%g' '%u'
# add group script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-groupadd '%g' && /usr/sbin/smbldap-groupshow %g|awk '/^gidNumber:/ {print $2}'
# delete group script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-groupdel '%g'
# The add machine script is use by a samba server configured as a domain
# controller to add local machine accounts when adding machines to the domain.
# The script must work from the command line when replacing the macros,
# or the operation will fail. Check that groups exist if forcing a group.
# Script for domain controller for adding machines:
# add machine script = /usr/sbin/useradd -d /dev/null -g machines -c 'Machine Account' -s /bin/false -M '%u'
# Script for domain controller with LDAP backend for adding machines (please
# configure in /etc/samba/smbldap_conf.pm first):
# add machine script = /usr/sbin/smbldap-useradd -w -d /dev/null -c 'Machine Account' -s /bin/false '%u'
# Domain groups:
# Domain groups are now configured by using the 'net groupmap' tool
# Enable priveleges, ie allowing members of Domain Admins to join machines
# to the domain
# enable privileges = yes
# Samba Password Database configuration:
# Samba now has runtime-configurable password database backends. Multiple
# passdb backends may be used, but users will only be added to the first one
# Default:
# passdb backend = tdbsam
# TDB backen with fallback to smbpasswd and guest
# passdb backend = tdbsam smbpasswd guest
# LDAP with fallback to smbpasswd guest
# Enable SSL by using an ldaps url, or enable tls with 'ldap ssl' below.
# passdb backend = ldapsam:ldaps://ldap.mydomain.com smbpasswd guest
# Use the samba2 LDAP schema:
# passdb backend = ldapsam_compat:ldaps://ldap.mydomain.com smbpasswd guest
# Idmap settings (set idmap uid and idmap gid above):
# Idmap backend to use:
# idmap backend = ldap:ldap://ldap.mydomain.com
# LDAP configuration for Domain Controlling:
# The account (dn) that samba uses to access the LDAP server
# This account needs to have write access to the LDAP tree
# You will need to give samba the password for this dn, by
# running 'smbpasswd -w mypassword'
# ldap admin dn = cn=root,dc=mydomain,dc=com
# ldap ssl = start_tls
# start_tls should run on 389, but samba defaults incorrectly to 636
# ldap port = 389
# ldap suffix = dc=mydomain,dc=com
# Seperate suffixes are available for machines, users, groups, and idmap, if
# ldap suffix appears first, it is appended to the specific suffix.
# Example for a unix-ish directory layout:
# ldap machine suffix = ou=Hosts
# ldap user suffix = ou=People
# ldap group suffix = ou=Group
# ldap idmap suffix = ou=Idmap
# Example for AD-ish layout:
# ldap machine suffix = cn=Computers
# ldap user suffix = cn=Users
# ldap group suffix = cn=Groups
# ldap idmap suffix = cn=Idmap
# 7. Name Resolution Options:
# All NetBIOS names must be resolved to IP Addresses
# 'Name Resolve Order' allows the named resolution mechanism to be specified
# the default order is "host lmhosts wins bcast". "host" means use the unix
# system gethostbyname() function call that will use either /etc/hosts OR
# DNS or NIS depending on the settings of /etc/host.config, /etc/nsswitch.conf
# and the /etc/resolv.conf file. "host" therefore is system configuration
# dependant. This parameter is most often of use to prevent DNS lookups
# in order to resolve NetBIOS names to IP Addresses. Use with care!
# The example below excludes use of name resolution for machines that are NOT
# on the local network segment
# - OR - are not deliberately to be known via lmhosts or via WINS.
# name resolve order = wins lmhosts bcast
# Windows Internet Name Serving Support Section:
# WINS Support - Tells the NMBD component of Samba to enable it's WINS Server
# wins support = yes
# WINS Server - Tells the NMBD components of Samba to be a WINS Client
# Note: Samba can be either a WINS Server, or a WINS Client, but NOT both
# wins server = w.x.y.z
# WINS Proxy - Tells Samba to answer name resolution queries on
# behalf of a non WINS capable client, for this to work there must be
# at least one WINS Server on the network. The default is NO.
# wins proxy = yes
# DNS Proxy - tells Samba whether or not to try to resolve NetBIOS names
# via DNS nslookups. The built-in default for versions 1.9.17 is yes,
# this has been changed in version 1.9.18 to no.
dns proxy = no
netbios name = MAGEIA
# 8. File Naming Options:
# Case Preservation can be handy - system default is _no_
# NOTE: These can be set on a per share basis
# preserve case = no
# short preserve case = no
# Default case is normally upper case for all DOS files
# default case = lower
# Be very careful with case sensitivity - it can break things!
# case sensitive = no
# Enabling internationalization:
# you can match a Windows code page with a UNIX character set.
# Windows: 437 (US), 737 (GREEK), 850 (Latin1 - Western European),
# 852 (Eastern Eu.), 861 (Icelandic), 932 (Cyrillic - Russian),
# 936 (Japanese - Shift-JIS), 936 (Simpl. Chinese), 949 (Korean Hangul),
# 950 (Trad. Chin.).
# UNIX: ISO8859-1 (Western European), ISO8859-2 (Eastern Eu.),
# ISO8859-5 (Russian Cyrillic), KOI8-R (Alt-Russ. Cyril.)
# This is an example for french users:
# dos charset = 850
# unix charset = ISO8859-1
#============================ Share Definitions ==============================
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
browseable = no
writable = yes
# You can enable VFS recycle bin and on-access virus-scanning on a per
# share basis:
# Uncomment the next 2 lines (make sure you create a .recycle folder in
# the base of the share and ensure all users will have write access to it.
# For virus scanning, install samba-vscan-clamav and ensure the clamd service
# is running
# vfs objects = vscan-clamav recycle
# vscan-clamav: config-file = /etc/samba/vscan-clamav.conf
# Un-comment the following and create the netlogon directory for Domain Logons
# [netlogon]
# comment = Network Logon Service
# path = /var/lib/samba/netlogon
# guest ok = yes
# writable = no
#Uncomment the following 2 lines if you would like your login scripts to
#be created dynamically by ntlogon (check that you have it in the correct
#location (the default of the ntlogon rpm available in contribs)
#root preexec = /usr/bin/ntlogon -u '%u' -g '%g' -o %a -d /var/lib/samba/netlogon/
#root postexec = rm -f '/var/lib/samba/netlogon/%u.bat'
# Un-comment the following to provide a specific roving profile share
# the default is to use the user's home directory
#[Profiles]
# path = /var/lib/samba/profiles
# browseable = no
# guest ok = yes
# writable = yes
# This script can be enabled to create profile directories on the fly
# You may want to turn off guest acces if you enable this, as it
# hasn't been thoroughly tested.
#root preexec = PROFILE='/var/lib/samba/profiles/%u'; if [ ! -e $PROFILE ];
# then mkdir -pm700 $PROFILE; chown '%u':'%g' $PROFILE;fi
# If you want read-only profiles, fake permissions so windows clients think
# they have written to the files
# vfs objects = fake_perms
# NOTE: If you have a CUPS print system there is no need to
# specifically define each individual printer.
# You must configure the samba printers with the appropriate Windows
# drivers on your Windows clients or upload the printer driver to the
# server from Windows (NT/2000/XP). On the Samba server no filtering is
# done. If you wish that the server provides the driver and the clients
# send PostScript ("Generic PostScript Printer" under Windows), you have
# to use 'printcap name = cups' or swap the 'print command' line below
# with the commented one. Note that print commands only work if not using
# 'printing=cups'
[printers]
comment = All Printers
path = /var/spool/samba
browseable = no
# to allow user 'guest account' to print.
guest ok = yes
writable = no
printable = yes
create mode = 0700
# =====================================
# print command: see above for details.
# =====================================
print command = lpr-cups -P %p -o raw %s -r # using client side printer drivers.
# print command = lpr-cups -P %p %s # using cups own drivers (use generic PostScript on clients).
# If you install drivers on the server, you will want to uncomment this so
# clients request the driver
use client driver = yes
# This share is used for Windows NT-style point-and-print support.
# To be able to install drivers, you need to be either root, or listed
# in the printer admin parameter above. Note that you also need write access
# to the directory and share definition to be able to upload the drivers.
# For more information on this, please see the Printing Support Section of
# /usr/share/doc/samba-<version>/docs/Samba-HOWTO-Collection.pdf
#
# A special case is using the CUPS Windows Postscript driver, which allows
# all features available via CUPS on the client, by publishing the ppd file
# and the cups driver by using the 'cupsaddsmb' tool. This requires the
# installation of the CUPS driver (http://www.cups.org/windows.php)
# on the server, but doesn't require you to use Windows at all :-).
[print$]
path = /var/lib/samba/printers
browseable = yes
write list = @adm root
guest ok = yes
inherit permissions = yes
# Settings suitable for Winbind:
# write list = @"Domain Admins" root
# force group = +@"Domain Admins"
# A useful application of samba is to make a PDF-generation service
# To streamline this, install windows postscript drivers (preferably colour)
# on the samba server, so that clients can automatically install them.
# Note that this only works if 'printing' is *not* set to 'cups'
[pdf-gen]
path = /var/tmp
guest ok = No
printable = Yes
comment = PDF Generator (only valid users)
printing = bsd
#print command = /usr/share/samba/scripts/print-pdf file path win_path recipient IP &
print command = /usr/share/samba/scripts/print-pdf "%s" "%H" "//%L/%u" "%m" "%I" "%J" &
lpq command = /bin/true
[PARTAGE]
path = /home/adrien/PARTAGE
comment = "PartageWindows"
browseable = yes
hide dot files = yes
read only = no
public = yes
writable = yes
Oui évidemment, le pare-feu est autorisé. (même en désactivant la totalité du pare-feu cela ne fonctionne pas).
Sur moi même ça marche pas ( smb://127.0.0.1/PARTAGE/ )
A distance depuis mon autre PC de test Mageia ( smb://192.168.1.21/PARTAGE/ )
Depuis un autre PC Windows cela ne fonctionne pas.
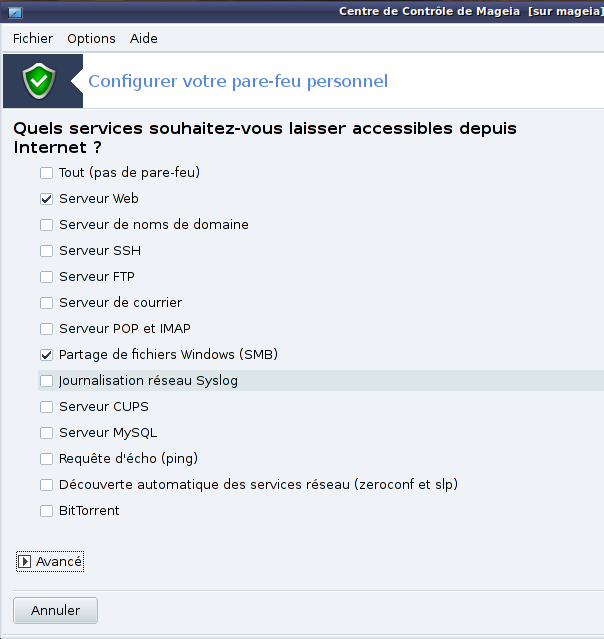
PARE-FEU:
A noter que le serveur web fonctionne bien lui et est accessible depuis un autre PC.
Il doit y avoir un truc qui m'échappe ... Pourtant, je l'ai fait plein de fois, et l'administration système, je sais ce que c'est je suis en plein dedans.
Édité par Adrien.D Le 10/12/2011 à 15h10
Config : PC Fixe : X470 GAMING PRO- AMD Ryzen 5 2600X - 16Go RAM - Radeon RX 560 (Pilote libre) - Gentoo Linux - GNOME Desktop - Kernel 5.10 LTS
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !

Polo35 Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Polo35
- Inscrit le : 01/06/2011
- Groupes :
la commande (sous root) # service smb status doit répondre au minimum :
Code BASH :
service smb status
smbd (pid 3784) est en cours d'exécution...
nmbd (pid 3799) est en cours d'exécution...
Si oui, que donne la commande
Code BASH :
smbclient -L localhostAs-tu validé ton fichier smb.conf avec la commande
Code BASH :
testparm
Édité par Polo35 Le 10/12/2011 à 19h01
Mageia 9 64 bits, Plasma
Yopman Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Yopman
- Inscrit le : 24/12/2008
- Site internet
- Groupes :
-
Administrateur

Je vais y jeter un oeil
Ton testparm en console est propre ?

Adrien.D Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Adrien.D
- Inscrit le : 30/05/2011
- Site internet
- Groupes :
Caché :
16 [18:24:24] root@mageia: /usr/lib64/mumble # service smb status
smbd (pid 24065) est en cours d'exécution...
nmbd (pid 24073) est en cours d'exécution...
smbd (pid 24065) est en cours d'exécution...
nmbd (pid 24073) est en cours d'exécution...
Caché :
17 [18:26:36] root@mageia: /usr/lib64/mumble # smbclient -L locahost
Enter adrien's password:
Connection to locahost failed (Error NT_STATUS_BAD_NETWORK_NAME)
18 [18:27:35] root@mageia: /usr/lib64/mumble # smbclient -L mageia
Enter adrien's password:
Domain=[WORKGROUP] OS=[Unix] Server=[Samba 3.5.8]
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (mageia)
PARTAGE Disk PartageWindows
pdf-gen Printer PDF Generator (only valid users)
print$ Disk
HP-Photosmart-C5300-series Printer HP Photosmart C5300 series
Domain=[WORKGROUP] OS=[Unix] Server=[Samba 3.5.8]
Server Comment
--------- -------
MAGEIA mageia
Workgroup Master
--------- -------
MAISON PORTABLE
WORKGROUP MAGEIA
19 [18:27:46] root@mageia: /usr/lib64/mumble #
Enter adrien's password:
Connection to locahost failed (Error NT_STATUS_BAD_NETWORK_NAME)
18 [18:27:35] root@mageia: /usr/lib64/mumble # smbclient -L mageia
Enter adrien's password:
Domain=[WORKGROUP] OS=[Unix] Server=[Samba 3.5.8]
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (mageia)
PARTAGE Disk PartageWindows
pdf-gen Printer PDF Generator (only valid users)
print$ Disk
HP-Photosmart-C5300-series Printer HP Photosmart C5300 series
Domain=[WORKGROUP] OS=[Unix] Server=[Samba 3.5.8]
Server Comment
--------- -------
MAGEIA mageia
Workgroup Master
--------- -------
MAISON PORTABLE
WORKGROUP MAGEIA
19 [18:27:46] root@mageia: /usr/lib64/mumble #
Caché :
19 [18:27:46] root@mageia: /usr/lib64/mumble # testparm
Load smb config files from /etc/samba/smb.conf
rlimit_max: increasing rlimit_max (1024) to minimum Windows limit (16384)
Processing section "[homes]"
Processing section "[printers]"
Processing section "[print$]"
Processing section "[pdf-gen]"
Processing section "[PARTAGE]"
Loaded services file OK.
Warning: Service printers defines a print command, but rameter is ignored when using CUPS libraries.
Server role: ROLE_STANDALONE
Press enter to see a dump of your service definitions
[global]
server string = %h
map to guest = Bad User
log file = /var/log/samba/%m.log
max log size = 50
printcap cache time = 60
printcap name = cups
dns proxy = No
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
read only = No
browseable = No
[printers]
comment = All Printers
path = /var/spool/samba
create mask = 0700
guest ok = Yes
printable = Yes
print command = lpr-cups -P %p -o raw %s -r # using client side printer drivers.
use client driver = Yes
browseable = No
[print$]
path = /var/lib/samba/printers
write list = @adm, root
inherit permissions = Yes
guest ok = Yes
[pdf-gen]
comment = PDF Generator (only valid users)
path = /var/tmp
printable = Yes
printing = bsd
print command = /usr/share/samba/scripts/print-pdf "%s" "%H" "//%L/%u" "%m" "%I" "%J" &
lpq command = /bin/true
lprm command = lprm -P'%p' %j
[PARTAGE]
comment = "PartageWindows"
path = /home/adrien/PARTAGE
read only = No
guest ok = Yes
20 [18:28:32] root@mageia: /usr/lib64/mumble #
Load smb config files from /etc/samba/smb.conf
rlimit_max: increasing rlimit_max (1024) to minimum Windows limit (16384)
Processing section "[homes]"
Processing section "[printers]"
Processing section "[print$]"
Processing section "[pdf-gen]"
Processing section "[PARTAGE]"
Loaded services file OK.
Warning: Service printers defines a print command, but rameter is ignored when using CUPS libraries.
Server role: ROLE_STANDALONE
Press enter to see a dump of your service definitions
[global]
server string = %h
map to guest = Bad User
log file = /var/log/samba/%m.log
max log size = 50
printcap cache time = 60
printcap name = cups
dns proxy = No
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
read only = No
browseable = No
[printers]
comment = All Printers
path = /var/spool/samba
create mask = 0700
guest ok = Yes
printable = Yes
print command = lpr-cups -P %p -o raw %s -r # using client side printer drivers.
use client driver = Yes
browseable = No
[print$]
path = /var/lib/samba/printers
write list = @adm, root
inherit permissions = Yes
guest ok = Yes
[pdf-gen]
comment = PDF Generator (only valid users)
path = /var/tmp
printable = Yes
printing = bsd
print command = /usr/share/samba/scripts/print-pdf "%s" "%H" "//%L/%u" "%m" "%I" "%J" &
lpq command = /bin/true
lprm command = lprm -P'%p' %j
[PARTAGE]
comment = "PartageWindows"
path = /home/adrien/PARTAGE
read only = No
guest ok = Yes
20 [18:28:32] root@mageia: /usr/lib64/mumble #
Config : PC Fixe : X470 GAMING PRO- AMD Ryzen 5 2600X - 16Go RAM - Radeon RX 560 (Pilote libre) - Gentoo Linux - GNOME Desktop - Kernel 5.10 LTS
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !

xuo Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre xuo
- Inscrit le : 23/10/2011
- Groupes :
2 questions, 1 remarque :
- Mageia c'est le nom du serveur smb ? C'est lui qui va fournir le service à une machine Windows ?
- Vous lancez la commande smbclient en étant root et smbclient demande la mot de passe de l'utilisateur adrien. Comment cela se fait-il ?
- Le fait que smbclient réponde est plutôt encourageant. Le problème est que PARTAGE ne s'affiche pas dans Dolphin. C'est peut-être embêtant, mais ce n'est pas le but de la manip. J'ai toujours testé avec smbclient. C'est cela qui doit marcher. Maintenant,, il faut aller sur un PC Windows et voir si cela marche ou pas.
Xuo.
Adrien.D Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Adrien.D
- Inscrit le : 30/05/2011
- Site internet
- Groupes :
mageia est le nom d'hôte de la machine sur lequel samba-server est installé.
smbclient je ne sais pas ce que cela fait.
Que dois-je tester sur Windows ? les commandes smbclient ?
Config : PC Fixe : X470 GAMING PRO- AMD Ryzen 5 2600X - 16Go RAM - Radeon RX 560 (Pilote libre) - Gentoo Linux - GNOME Desktop - Kernel 5.10 LTS
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !

Polo35 Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Polo35
- Inscrit le : 01/06/2011
- Groupes :
Mageia 9 64 bits, Plasma
Adrien.D Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Adrien.D
- Inscrit le : 30/05/2011
- Site internet
- Groupes :
Caché :
Dec 10 22:42:14 mageia smbd[31096]: [2011/12/10 22:42:14.406432, 0] smbd/service.c:988(make_connection_snum)
Dec 10 22:42:14 mageia smbd[31096]: canonicalize_connect_path failed for service PARTAGE, path /home/adrien/PARTAGE
Dec 10 22:42:14 mageia smbd[31096]: canonicalize_connect_path failed for service PARTAGE, path /home/adrien/PARTAGE
humm ...
Édité par Adrien.D Le 10/12/2011 à 22h41
Config : PC Fixe : X470 GAMING PRO- AMD Ryzen 5 2600X - 16Go RAM - Radeon RX 560 (Pilote libre) - Gentoo Linux - GNOME Desktop - Kernel 5.10 LTS
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !

Polo35 Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Polo35
- Inscrit le : 01/06/2011
- Groupes :
Tous les répertoires doivent être exécutables pour pouvoir les parcourir.
Si ce n'est pas le cas alors
Code BASH :
chmod +x /home/adrien chmod +x /home/adrien/PARTAGE
Mageia 9 64 bits, Plasma
Adrien.D Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Adrien.D
- Inscrit le : 30/05/2011
- Site internet
- Groupes :
Mais cette vue la fonctionne:
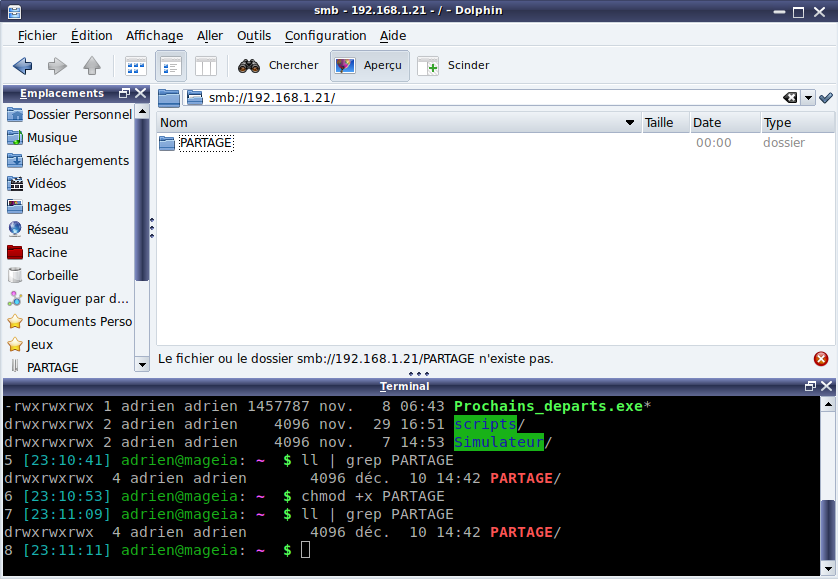
Si je clique sur PARTAGE, je suis dans le même cas qu'avant
Config : PC Fixe : X470 GAMING PRO- AMD Ryzen 5 2600X - 16Go RAM - Radeon RX 560 (Pilote libre) - Gentoo Linux - GNOME Desktop - Kernel 5.10 LTS
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !

Polo35 Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Polo35
- Inscrit le : 01/06/2011
- Groupes :
Code BASH :
adrien:500:15175F2E8D4679189C5014AE4718A7EE:DB3B561A039ED149B5B6DC7E04640AD9:[U ]:LCT-470CF70B:
Sinon il faut créer l'utilisateur samba :
Code BASH :
smbpasswd -a adrien
Mageia 9 64 bits, Plasma
Adrien.D Membre non connecté
-

- Voir le profil du membre Adrien.D
- Inscrit le : 30/05/2011
- Site internet
- Groupes :
Config : PC Fixe : X470 GAMING PRO- AMD Ryzen 5 2600X - 16Go RAM - Radeon RX 560 (Pilote libre) - Gentoo Linux - GNOME Desktop - Kernel 5.10 LTS
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !
Ancien Webmaster de MageiaLinuxOnline. Les remplaçants assurent !

Répondre
Vous n'êtes pas autorisé à écrire dans cette catégorie